Glossary
This manual is an introductory guide and does not assume any prior knowledge of the mammalian skeleton. However, osteological identification often necessitates an unavoidable amount of specialist vocabulary, so correct anatomical terminology has been maintained throughout to avoid ambiguity. The following table provides a list of common terms used in this volume and in other faunal reference books. Labelled diagrams of a quadruped (sheep) and biped (kangaroo) are also included to illustrate the articulation of major bones in different species (Figures 0.1 and 0.2).
| Anterior | Toward the front, analogous to ventral. |
| Appendicular | The part of the skeleton that contains the limbs. |
| Articulation | The place where two bones meet (often a joint). |
| Axial | The part of the skeleton that contains the trunk (and often head). |
| Biped | An animal that habitually walks on two legs. |
| Buccal | Facing the cheek. |
| Caudal | Toward the tail. |
| Cavity | An open area (analogous to a fossa). |
| Condyle | A rounded process at the point of articulation. |
| Cortical | The type of bone found in shafts of long bones and flat bones, also called lamellar bone. |
| Cranial | Toward the head. |
| Crest | A projecting ridge. |
| Deciduous teeth | Milk (baby) teeth. |
| Diaphysis | The shaft of a long bone (mid-section). |
| Diastema | A space between two teeth. |
| Distal | Away from the trunk of the body (along a limb). |
| Dorsal | Toward the back or of the back; analogous to posterior in humans. |
| Element | The type of bone (e.g. femur, scapula). |
| Epiphysis | The end of a long bone, attached to the diaphysis, which is unfused in juveniles. |
| Foramen | A hole or opening. |
| Fossa | A pit or depression (analogous to a cavity). |
| Inferior | Lower. |
| Lateral | To the side, away from the centre of an individual. |
| Lingual | Facing the tongue. |
| Longitudinal | Lengthwise. |
| Medial | Toward the middle or centre of an individual. |
| Occlusal | The biting or chewing surface of the teeth. |
| Posterior | Behind (analogous to dorsal in quadrupeds). |
| Post-cranial | Referring to all bones below the head. |
| Post-depositional | After burial. |
| Process | Any outgrowth or projection of bone. |
| Proximal | Toward the trunk of the body (along a limb). |
| Quadruped | An animal that habitually walks on four legs. |
| Superior | Above, top. |
| Taphonomy | Everything that happens to an individual between death and archaeological recovery (see in ‘Bone identification 101’, ‘Post-depositional processes’). |
| Tooth types | Most species have four major types of teeth: canines, incisors, molars and premolars. |
| Trabecular | Spongy bone, also called cancellous bone; found in the epiphysis of long bones, it acts as a cushion for joints. |
| Tubercle | Small, knob-like projection. |
| Tuberosity | Large, rough projection. |
| Ventral | Toward the stomach or the front; analogous to anterior. |
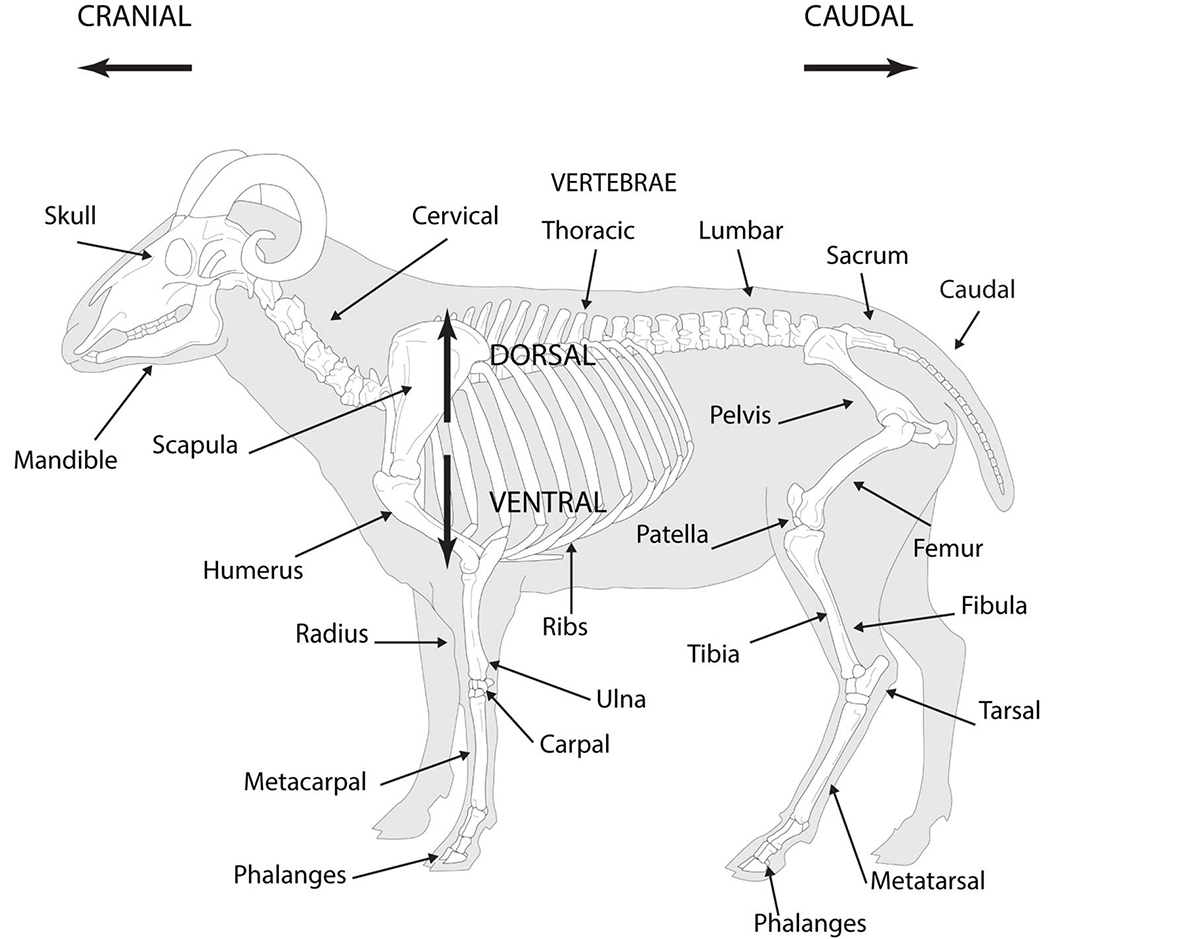
Figure 0.1: Articulated sheep skeleton, with bones and orientations labelled.
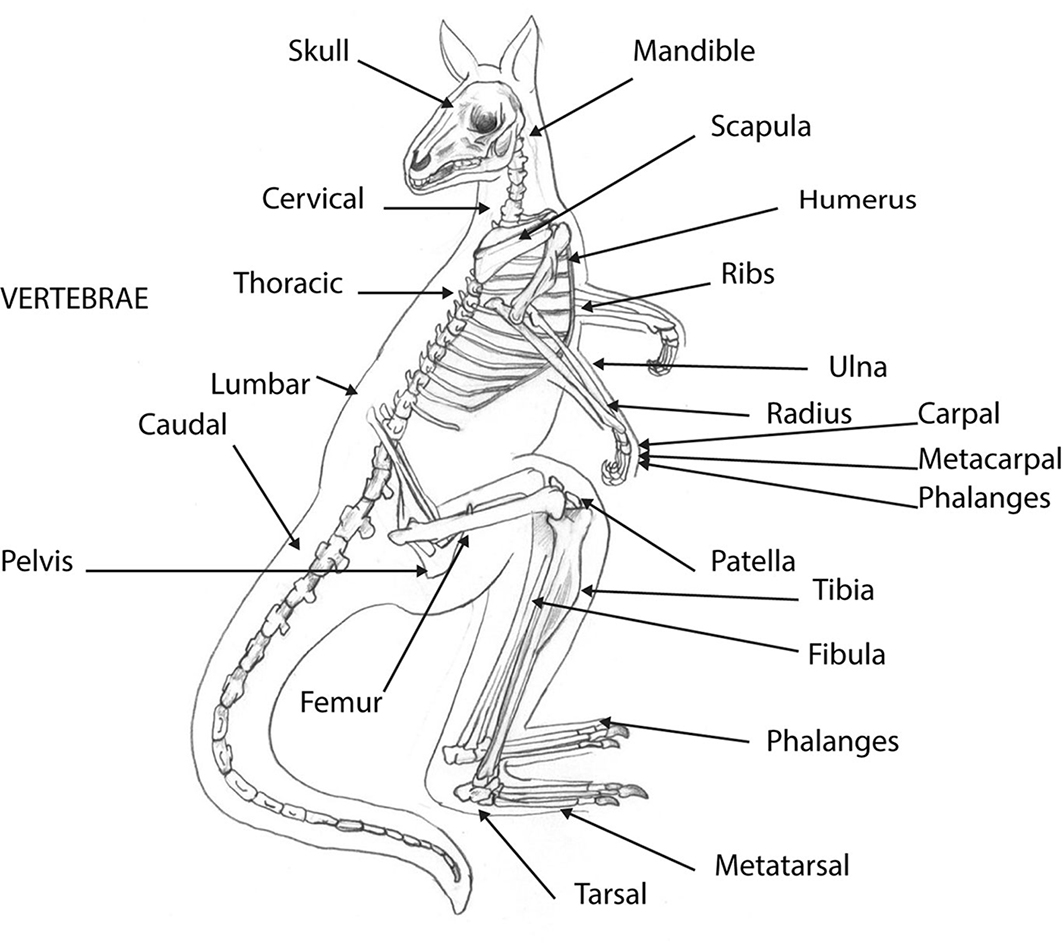
Figure 0.2: Articulated kangaroo skeleton, with bones labelled.